Nature—小胶质细胞研究重磅突破:小胶质细胞调控髓鞘生长并维持其完整性
2022-12-18 神经科学临床和基础 神经科学临床和基础 发表于安徽省
髓鞘是中枢神经系统神经元轴突功能所必需的,但支持髓鞘正常生理功能的机制尚不清楚。中枢神经系统中的巨噬细胞与髓鞘生理功能密切相关,但尚不清楚哪些巨噬细胞群参与其中,以及它们影响髓鞘生理的哪些过程。
 中文摘要
中文摘要
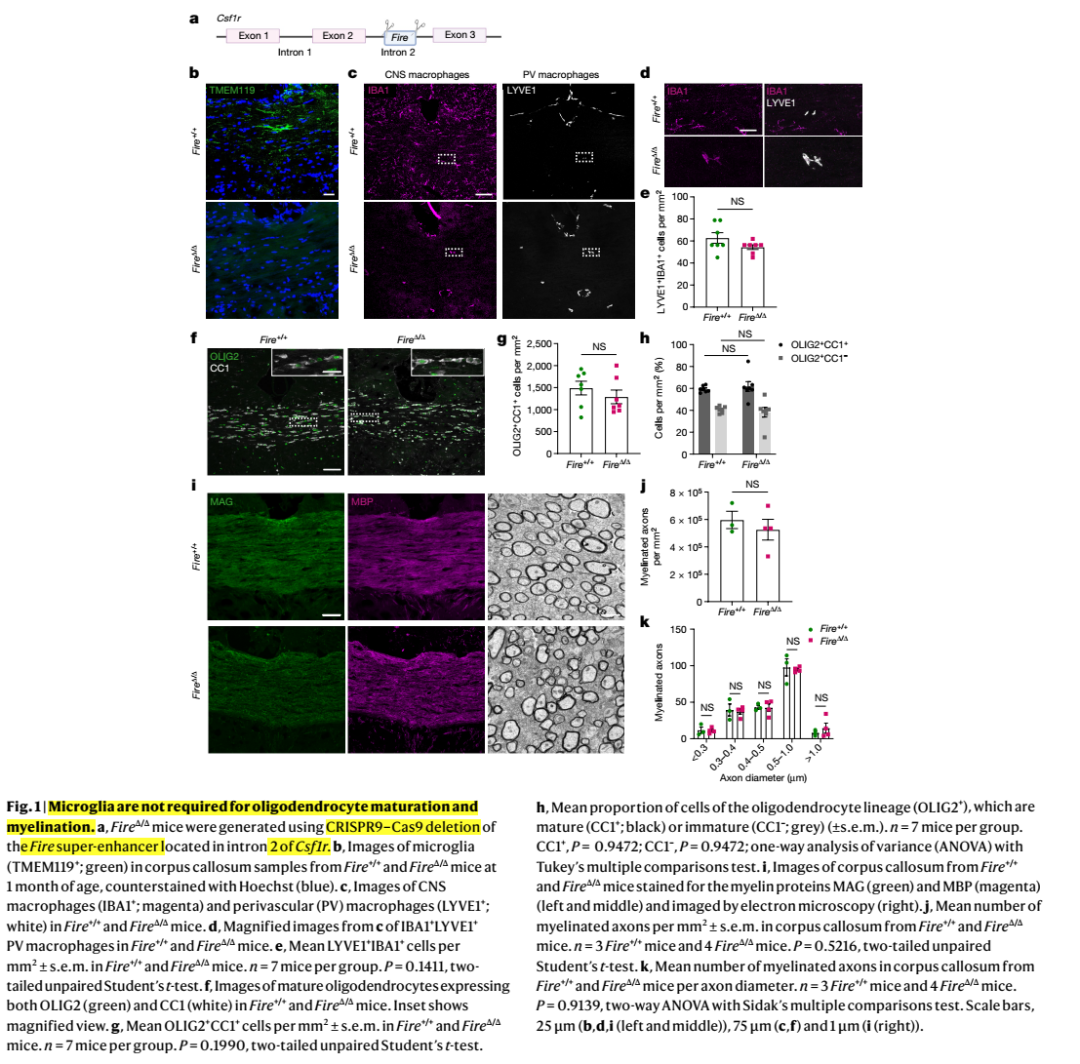
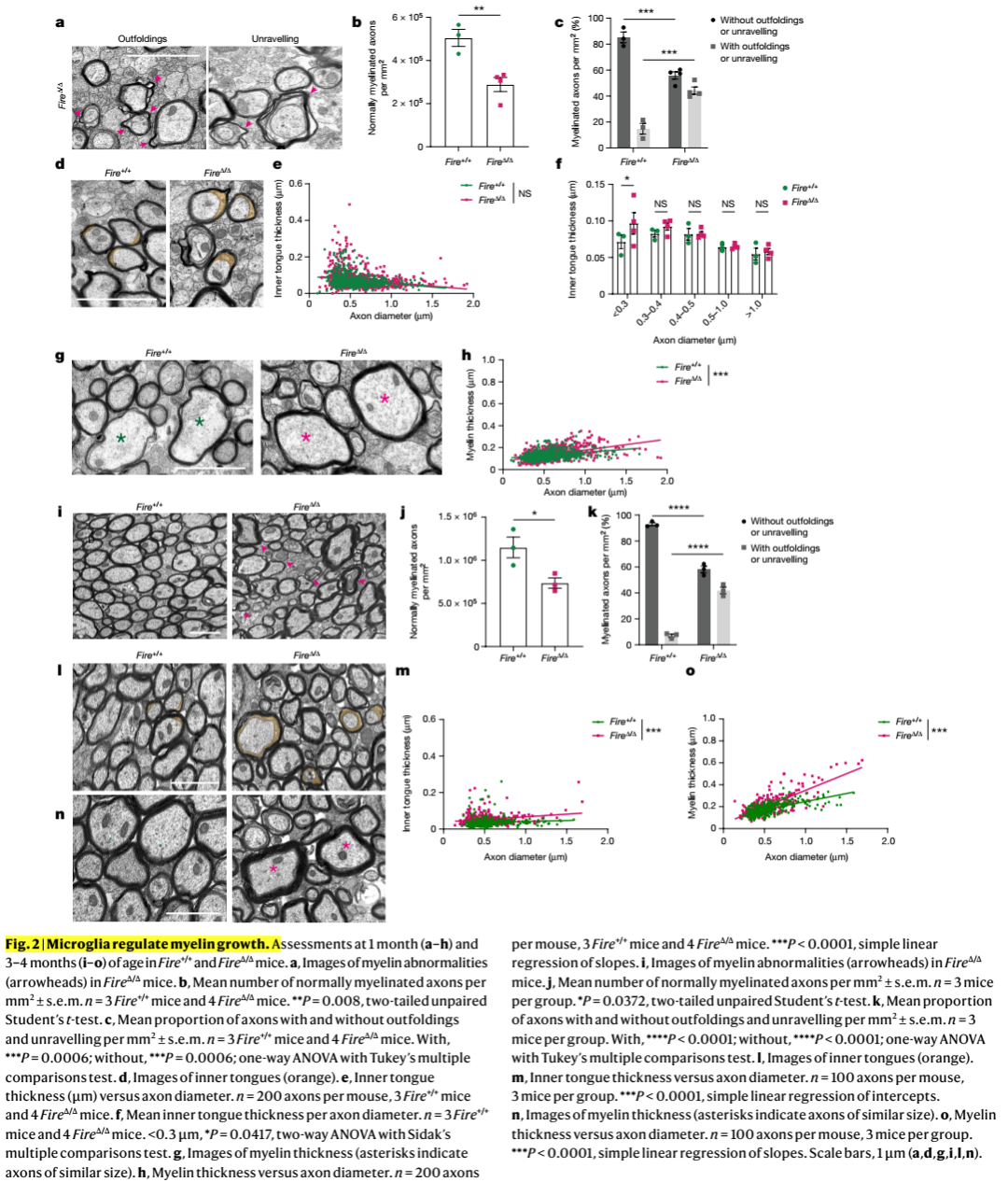
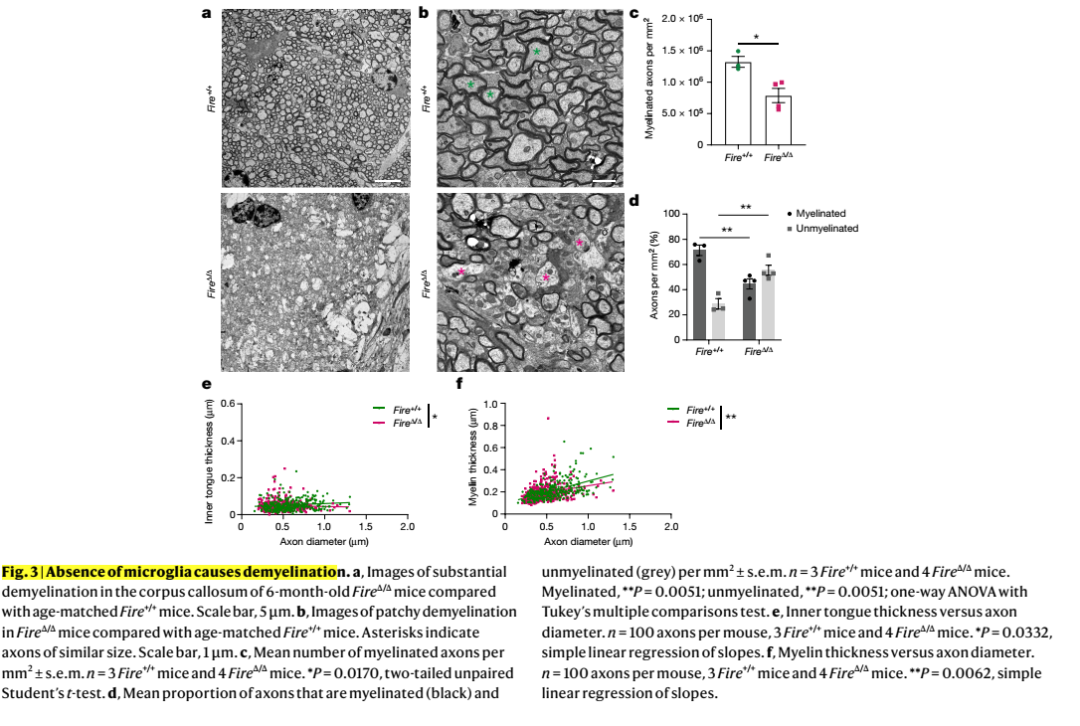
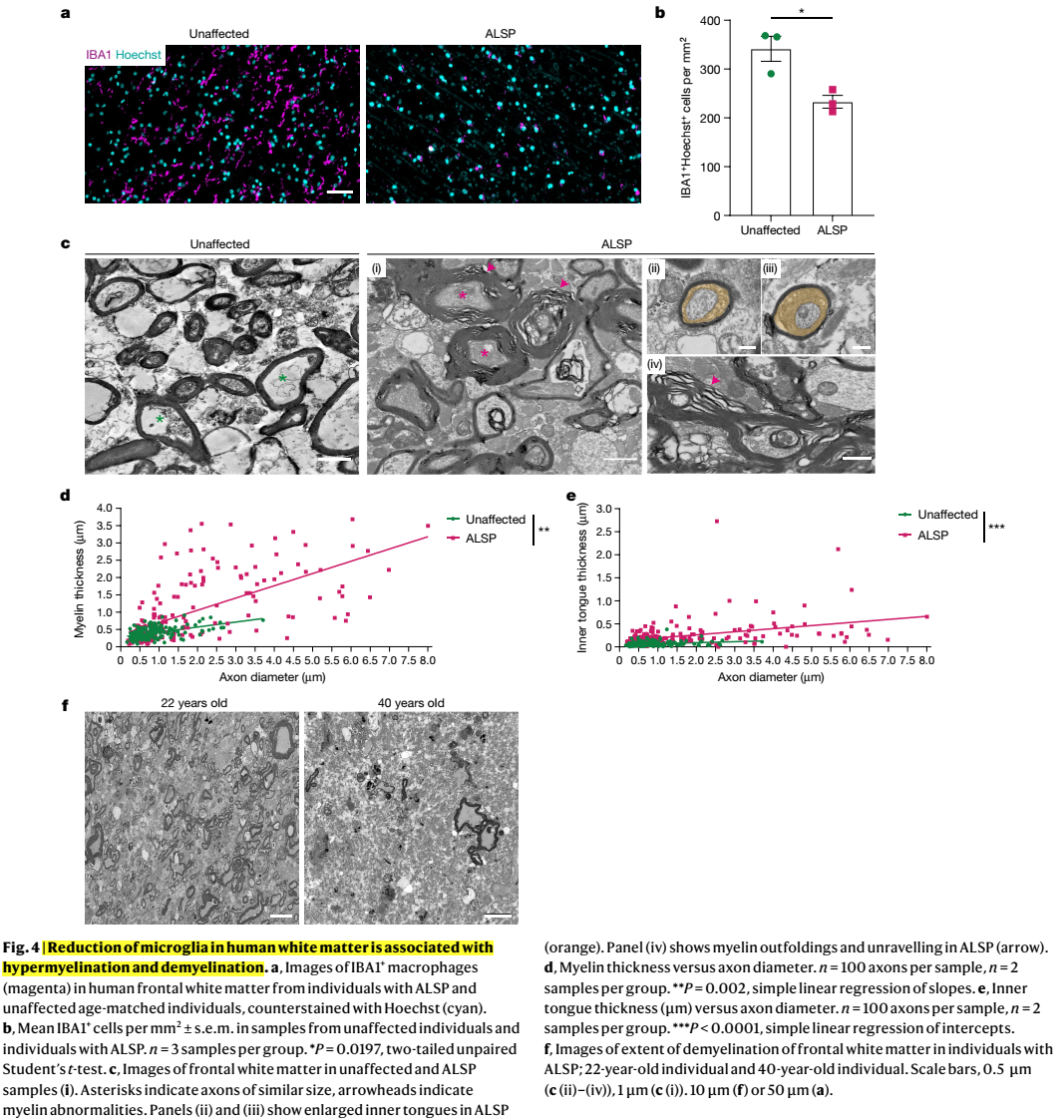
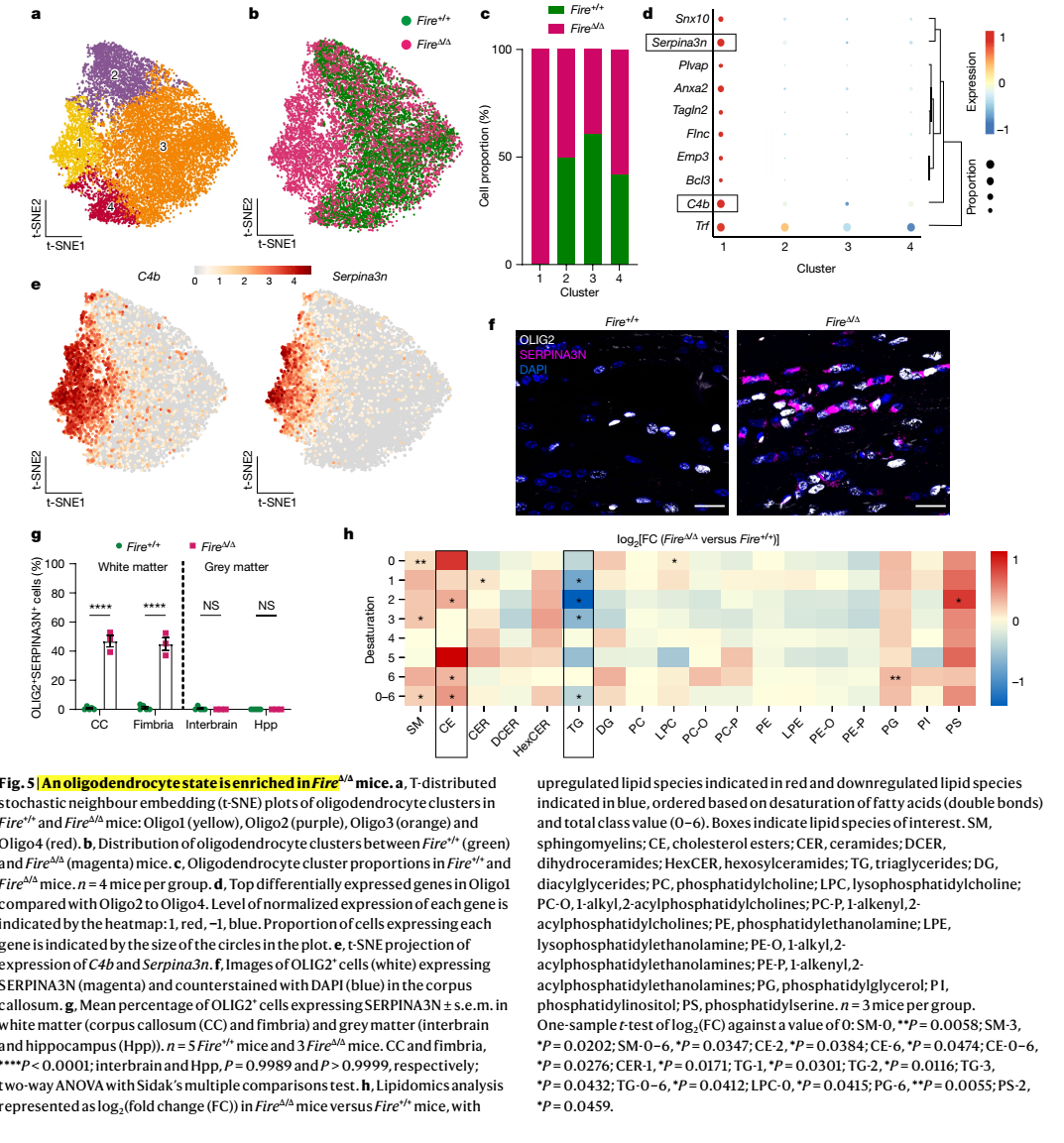
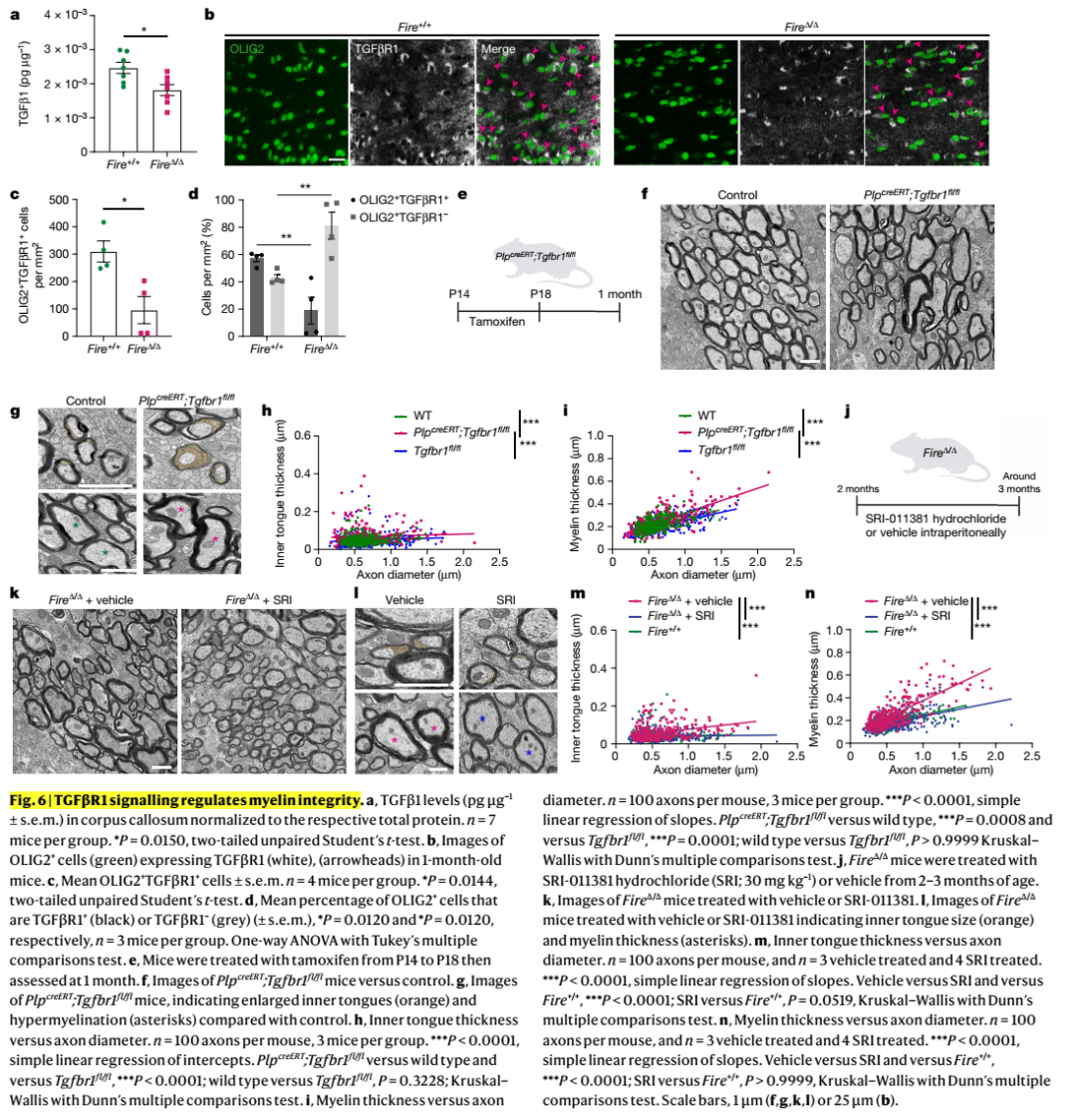
髓鞘是中枢神经系统神经元轴突功能所必需的,但支持髓鞘正常生理功能的机制尚不清楚。中枢神经系统中的巨噬细胞与髓鞘生理功能密切相关,但尚不清楚哪些巨噬细胞群参与其中,以及它们影响髓鞘生理的哪些过程。在这里,科学家发现,在小鼠和人类成年期,驻留的小胶质细胞对维持髓鞘生理至关重要。他们证明小胶质细胞对于髓鞘的发育是可有可无的。然而,它们是发育完成后调节髓鞘生长和相关认知功能以及通过防止髓鞘变性来保持髓鞘生理完整性所必需的。他们发现,由于缺少小胶质细胞而导致的髓鞘丢失与脂质代谢异常改变的少突胶质细胞的状态有关。此外,该机制通过破坏TGF-β1-TGF-βR1轴来进行调控。他们的研究结果表明,小胶质细胞是髓鞘生长和完整性异常的疾病(如衰老和神经退行性疾病)的理想治疗靶点。
英文摘要
Myelin is required for the function of neuronal axons in the central nervous system, but the mechanisms that support myelin health are unclear. Although macrophages in the central nervous system have been implicated in myelin health, it is unknown which macrophage populations are involved and which aspects they influence. Here we show that resident microglia are crucial for the maintenance of myelin health in adulthood in both mice and humans. We demonstrate that microglia are dispensable for developmental myelin ensheathment. However, they are required for subsequent regulation of myelin growth and associated cognitive function, and for preservation of myelin integrity by preventing its degeneration. We show that loss of myelin health due to the absence of microglia is associated with the appearance of a myelinating oligodendrocyte state with altered lipid metabolism. Moreover, this mechanism is regulated through disruption of the TGFβ1-TGFβR1 axis. Our findings highlight microglia as promising therapeutic targets for conditions in which myelin growth and integrity are dysregulated, such as in ageing and neurodegenerative disease.

本网站所有内容来源注明为“梅斯医学”或“MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于梅斯医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明来源为“梅斯医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,或“梅斯号”自媒体发布的文章,仅系出于传递更多信息之目的,本站仅负责审核内容合规,其内容不代表本站立场,本站不负责内容的准确性和版权。如果存在侵权、或不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言






