Oncogene:“TGF-β矛盾”促进或抑制乳腺癌生长机制
2012-02-24 towersimper MedSci原创
TGF-β的复杂细胞信号传导途径 信号告诉细胞表现得像癌细胞那样存活,生长和不受控制的增殖。信号也能够告诉带有癌变特征的细胞停止生长或死亡。在乳腺癌中,一种狡猾的称作TGF-β的信号发挥着两种作用:有时促进肿瘤产生,有时抑制肿瘤产生。 来自美国科罗拉多大学癌症研究中心的研究人员最近在Oncogene 期刊上发表一篇论文,详细地描述了肿瘤如何能够调控TGF-β信号传导开关,当它促进肿瘤产生时
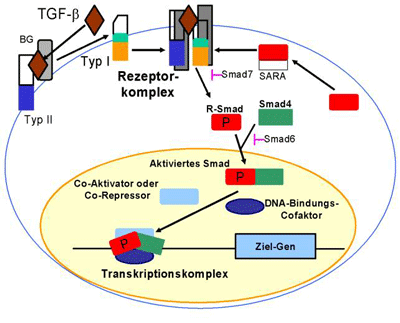
TGF-β的复杂细胞信号传导途径
信号告诉细胞表现得像癌细胞那样存活,生长和不受控制的增殖。信号也能够告诉带有癌变特征的细胞停止生长或死亡。在乳腺癌中,一种狡猾的称作TGF-β的信号发挥着两种作用:有时促进肿瘤产生,有时抑制肿瘤产生。
来自美国科罗拉多大学癌症研究中心的研究人员最近在Oncogene 期刊上发表一篇论文,详细地描述了肿瘤如何能够调控TGF-β信号传导开关,当它促进肿瘤产生时则允许医生完全阻断这种途径,而当它仍然起着抑制肿瘤生长时则让它保持完整。
科罗拉多大学癌症研究中心研究员、科罗拉多大学医学院妇产科副教授和该论文的通讯作者Heide Ford说,“本质上讲,肿瘤劫持一种胚胎程序,并启动这种程序。”
胚胎生长很快,因此需要细胞快速增殖并能够迁移到胚胎其他区域。在人发育早期,我们依赖一种称作SIX1的转录因子产生这种野草般疯狂生长和灵敏运动。
然后,成年时,我们的大多数细胞关闭这种SIX1途径,我们不再需要爆炸性生长或运动,因此这种途径在我们的基因组中沉睡下来。
大多数乳腺癌唤醒SIX1。这篇Oncogene 研究论文仔细描述了SIX1如何调控TGF-β信号传导开关,切换到抑制或促进肿瘤的状态。
SIX1产生调节基因活性的称作microRNAs的小分子。在这种情形中,SIX1产生的microRNAs附着到并减弱TGF-β中阻止细胞生长的氨基酸序列部分。当TGF-β被沉默时,这种信号并不阻止细胞生长,相反促进这些细胞迁移到新的组织。表达SIX1和与它相关联的microRNAs就像是移除鲁莽青少年驾驶的福特野马敞篷车(Mustang convertible)的限速器。
Ford说,“高水平的SIX1或与SIX1相关联的microRNAs是乳腺癌正在利用TGF-β信号传导促进肿瘤生长的征兆。”病人患上的乳腺癌若拥有高水平的SIX1或与SIX1相关联的microRNAs,那么肿瘤患者可能得益于“TGF-β抑制剂”,因为这种药物能够关闭这种信号,而且当前正在进行临床试验。相反,拥有低水平SIX1的乳腺癌患者最好保持TGF-β信号传导完整,在这种情形中,这种信号有可能帮助这些乳腺癌患者对抗她们的肿瘤。
在未来,Ford希望直接靶向SIX1。
她说,“因为在大多数成熟组织中我们不需要SIX1,如果我们能够靶向SIX1,我们就可能能够在多个战场抑制肿瘤生长同时很少有副作用。”
如今因发现靶标SIX,Ford和她的同事们正开发新药物阻止这种促进肿瘤生长的因子发挥作用。
拓展阅读---治疗学中的矛盾:

doi10.1038/onc.2012.11
The miR-106b-25 cluster targets Smad7, activates TGF-β signaling, and induces EMT and tumor initiating cell characteristics downstream of Six1 in human breast cancer
A L Smith, R Iwanaga, D J Drasin, D S Micalizzi, R L Vartuli, A-C Tan and H L Ford
The role of TGF-β signaling in tumorigenesis is paradoxical: it can be tumor suppressive or tumor promotional, depending on context. The metastatic regulator, Six1, was recently shown to mediate this switch, providing a novel means to explain this elusive ‘TGF-β paradox’. Herein, we identify a mechanism by which Six1 activates the tumor promotional arm of TGF-β signaling, via its ability to upregulate the miR-106b-25 microRNA cluster, and further identify a novel function for this cluster of microRNAs. Although expression of the miR-106b-25 cluster is known to overcome TGF-β-mediated growth suppression via targeting p21 and BIM, we demonstrate for the first time that this same cluster can additionally target the inhibitory Smad7 protein, resulting in increased levels of the TGF-β type I receptor and downstream activation of TGF-β signaling. We further show that the miR-106b-25 cluster is sufficient to induce an epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and a tumor initiating cell phenotype, and that it is required downstream of Six1 to induce these phenotypes. Finally, we demonstrate a significant correlation between miR-106b, Six1, and activated TGF-β signaling in human breast cancers, and further show that high levels of miR-106b and miR-93 in breast tumors significantly predicts shortened time to relapse. These findings expand the spectrum of oncogenic functions of miR-106b-25, and may provide a novel molecular explanation, through the Six1 regulated miR-106b-25 cluster, by which TGF-β signaling shifts from tumor suppressive to tumor promoting.
本网站所有内容来源注明为“梅斯医学”或“MedSci原创”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于梅斯医学所有。非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明来源为“梅斯医学”。其它来源的文章系转载文章,或“梅斯号”自媒体发布的文章,仅系出于传递更多信息之目的,本站仅负责审核内容合规,其内容不代表本站立场,本站不负责内容的准确性和版权。如果存在侵权、或不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。
在此留言








#TGF#
0
#Gene#
73
#TGF-β#
61
#Oncogene#
61